How to Control the Precision of CNC Milling Machining
March 1, 2024
How to Control the Precision of CNC Milling Machining
The quality of CNC machined parts depends on many factors, including part design, tool selection, tool path programming, machinist skill set, workpiece clamping strategy, Position Accuracy, etc.
Follow these methods of improving CNC machine accuracy and productivity. get the most out of the equipment you have and increase your project precision.
1. Mechanical Design
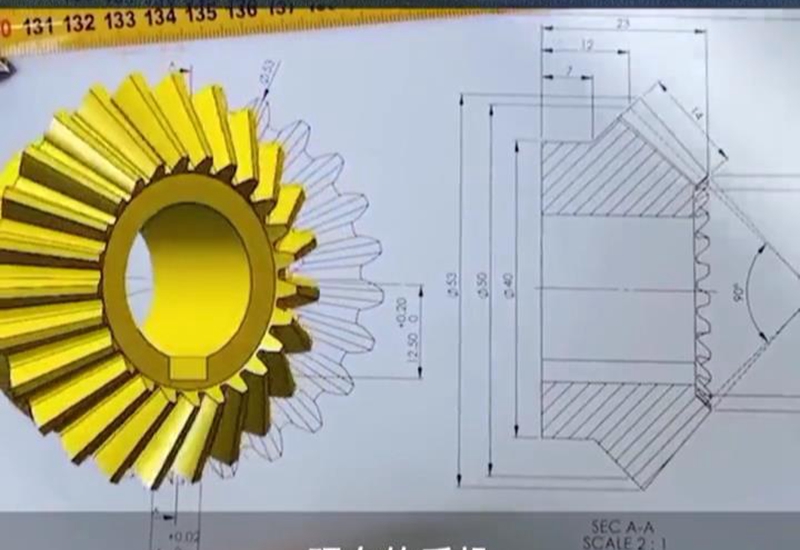
The complexity of the part design and the number of sides your machine works on affect the speed, precision, and accuracy of your work. One of the fastest ways to improve your CNC machining speed and accuracy is through an upgrade to a five-axis machine. If you have a three-axis device, for instance, you may waste time with extra setups during production time.
When you have a machine that works on more axes, you can save time for a speedier turnaround of part production. Also, you won’t need to worry about mistakes made during multiple setups.
For operations that already have a three-axis machine, integrating work on five sides can happen if you add a two-axis table to move the part. This 3+2 configuration offers the most straightforward, least expensive way to get machining on more sides of the component. However, if you must work on heavy or large parts, the table may not hold them as needed, and an upgrade to a five-axis machine may prove the best option for your operation.
2. Tool selection
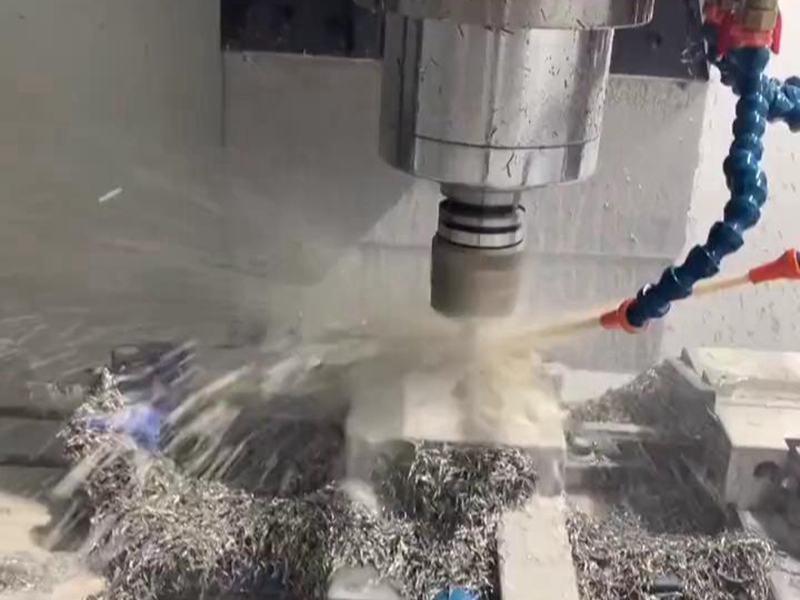

Although tool movements in CNC milling are automated, quality tools also add value to it. Make sure that you are using tools that are designed for the specific type of cutting. You should also regularly calibrate your machine tools to ensure that they are operated with the highest degree of precision.
Understand the Material Properties:
The material properties such as the tensile strength, yield strength, Young’s Modulus, and thermal expansion of the workpiece need to be considered while machining. For example, a low-yield strength material would deform more than a high-yield strength material when subjected to the same cutting force.
Upgrade the Machine Tool Promptly:
Nowadays, CNC machine manufacturers add new features and regularly update their firmware to improve productivity. Users may promptly upgrade them to optimize the value of their investments. However, they are reluctant to upgrade the machine tools due to the high investments involved. This may lead to part deformities or machining errors, which may increase product recalls.
Improve Cutting Tool:
Improving cutting tools means using a specifically designed tool for the type of material to be machined. There are different types of cutting tools available, so you should select the one that is best suited for your application to achieve the expected level of accuracy and precision.
Watch an Eye on Tool Wear:
Tool wear results from the abrasive contact between the tool and the workpiece. It causes a decrease in the size of the tooltip and a change in the shape of the tool cutting edge. This can cause the tool to cut inaccurately and produce poor-quality parts.
3. Tool path programming
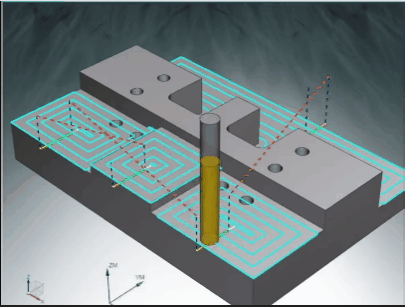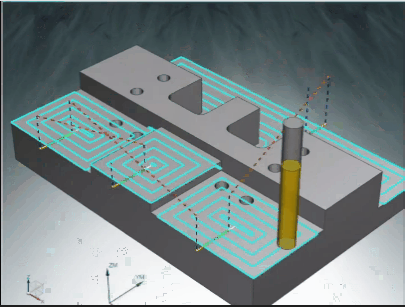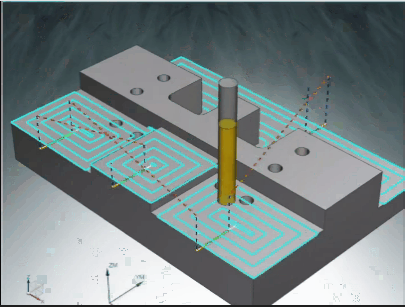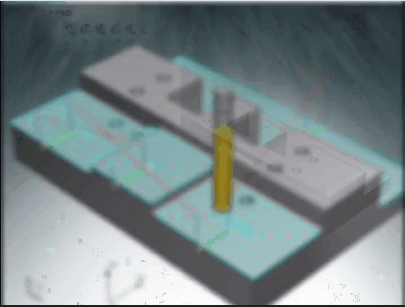
Skilled manufacturing engineers understand how to use different tools, with different methods and speeds, to efficiently manufacture precise CNC milled parts.
Whenever parts are set up on the rolling mill, a high-quality machining shop should have a documented first article inspection process. It will also have regular checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process for quality control.
4. Machinist skill set

Experienced machinists are more likely to understand the nuances that lead to the manufacture of precise parts.
5. Workpiece Clamping
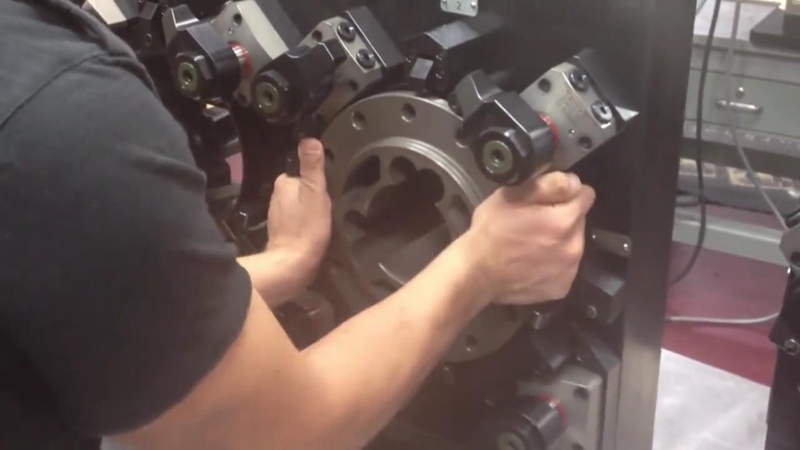
To minimize vibration and ensure accuracy, the shop must use proper workpiece clamping settings to hold the workpiece in place for processing.
Accuracy Of CNC Milling: 3 Measurements
Three different measurements determine the overall accuracy of the milled part: position accuracy, accuracy or repeatability, and tolerance.
6. Position Accuracy
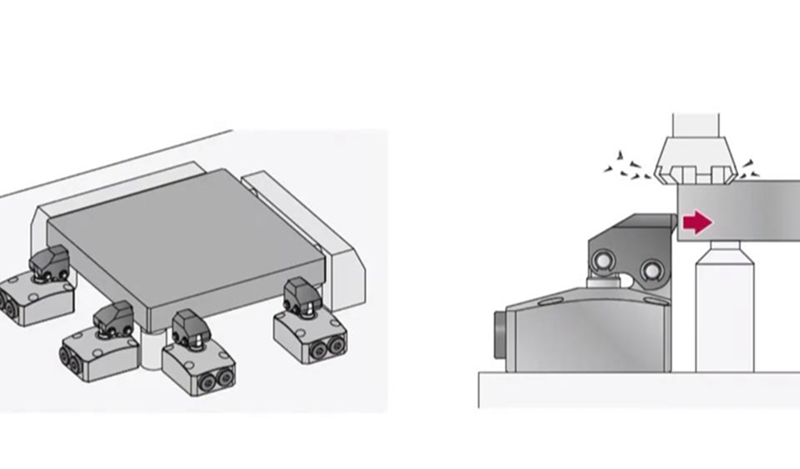
The position accuracy is equal to the difference between the specified distance between the points on the part and the actual measured distance of these points after milling. For a CNC milling machine, accuracy depends on its ability to follow its programmed path. The machining shop determines the accuracy of the rolling mill by taking multiple measurements and calculating the statistical average of the deviations.
Repeatable Accuracy
The machining shop defines the accuracy of the milling machine by precisely repeating the same commands so that one part after the other provides the same result. Similar to accuracy, the workshop can calculate the accuracy of the CNC milling machine through multiple measurements when commanding the machine’s cutting path. The measure of accuracy lies in the repeatability of cutting the same precise path, resulting in an accurate copy of the part over and over again.
Finished Product Tolerance
Machinists and engineers use the term tolerance when referring to the allowable deviation from the CNC milling machine to measure the set value. CNC programmers and machinists program the milling machine to manufacture parts within the tolerances required by the customer. When cutting materials and producing parts, the milling machine should stay within the set tolerance of the specified measurement value.
To produce the highest quality parts and products, all aspects of the machining process must be done with high accuracy. Every step must be precise from machine programming to the actual parts machining to achieve the desired results. Any slight inaccuracy can lead to faulty products that affect the manufacturer’s reputation but also put the consumers’ safety at risk.





