The Benefits of CNC Machining over 3D Printing
September 10, 2024
As technology progresses, it revolutionizes the manufacturing industry especially engineering and the pieces of machinery. In order to be the leader, you must use the best equipment to lead the business forward. Some of these advancements in the manufacturing process are computer numeric control (CNC) machining and 3D printing. Both work with varied materials but how can we determine the one we need?
CNC machining and 3D printing each have their strengths and weaknesses, offering unique benefits depending on the application. The decision between the two depends on factors such as material compatibility, production speed, precision, cost, and the quality of the final product. Understanding the key differences between CNC machining and 3D printing is essential to making the best choice for a manufacturing project.
Key Differences Between CNC Machining and 3D Printing
While CNC machining and 3D printing both enable manufacturers to produce complex parts, they operate on different principles. CNC machining is a subtractive process, where material is removed from a solid block to create a part, while 3D printing is an additive process, where material is deposited layer by layer to build the desired shape. These fundamental differences result in contrasting performance characteristics and applications.
1. Material Compatibility:
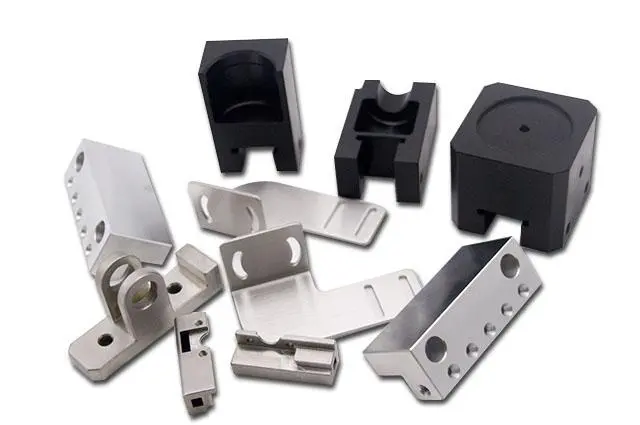

CNC machining is highly versatile and capable of working with a wide range of materials, including metals (aluminum, steel, titanium), plastics, wood, and composites. This makes CNC machining ideal for industries that require durable, heat-resistant, or structurally robust materials, such as aerospace, automotive, and industrial manufacturing.
.3D printing, on the other hand, is more limited in its material selection. Although newer 3D printers can handle certain metals and ceramics, most 3D printing is done with plastics (such as ABS or PLA), resins, or nylon. The mechanical properties of these materials often limit the application of 3D-printed parts in demanding environments.
2. Production Speed and Volume:
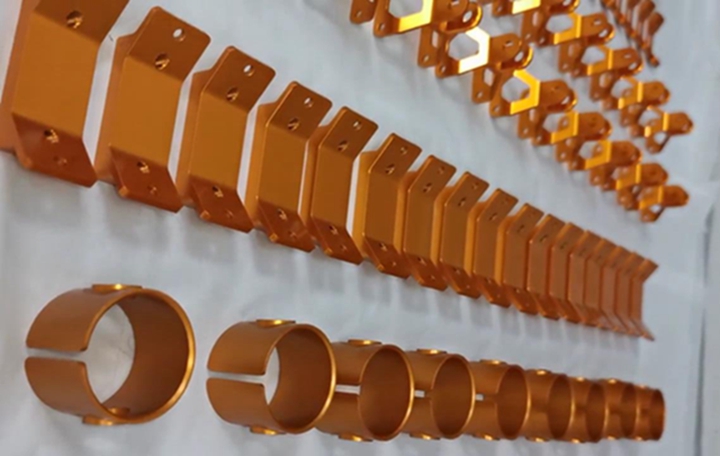

. CNC machining is often the preferred choice for mass production due to its speed. CNC machines can rapidly produce large quantities of parts with minimal variation, making them ideal for high-volume manufacturing. In many cases, CNC machines can complete the production of a part in a matter of minutes.
.In contrast, 3D printing can be slow, especially when printing large or intricate parts. Since 3D printing is an additive process, the machine must build the product layer by layer, which can take hours or even days depending on the complexity of the design. This makes 3D printing less efficient for high-volume production but useful for creating custom, one-off designs or prototypes.
3. Precision and Tolerance:
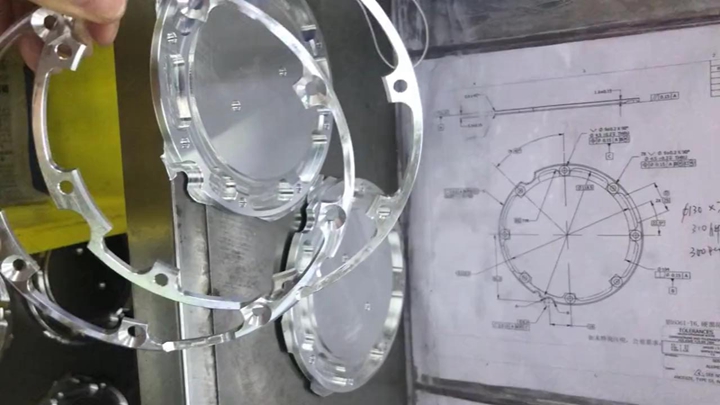
. CNC machines are known for their high precision and tight tolerances, making them ideal for parts that require exact measurements and perfect fits. The subtractive nature of CNC machining allows for extremely fine detailing, with tolerances as tight as ±0.005 inches or better.
. 3D printing, while improving in precision, generally cannot match the tight tolerances of CNC machining. The layer-by-layer construction of 3D printing introduces slight variations in dimensions, which can lead to parts that do not meet stringent accuracy requirements, particularly for interlocking or moving components.
4. Surface Finish:
. Parts produced by CNC machining typically have a smooth, clean surface finish because the process involves cutting and shaping a solid material. CNC machines can create parts with minimal post-processing and excellent surface quality, making them suitable for products where aesthetics are important, such as consumer electronics or medical devices.
. By contrast, 3D-printed parts often require additional post-processing to achieve a smooth finish. The layered construction can result in visible lines, rough surfaces, or small defects, which may need to be sanded or polished away. This added step increases the time and cost of production.
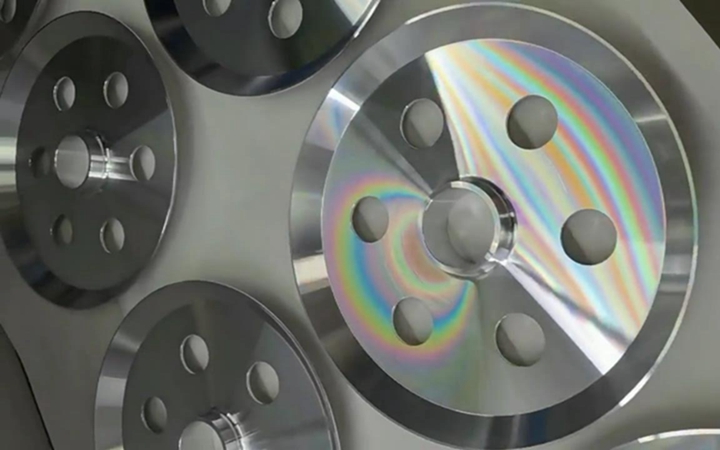

The Advantages of CNC Machining Over 3D Printing
When comparing CNC machining and 3D printing, it is clear that CNC machining holds several advantages, especially for high-volume production, durable materials, and applications where precision and structural integrity are paramount. While 3D printing is well-suited to prototyping and low-volume custom designs, CNC machining remains the go-to solution for many industries seeking efficiency, strength, and cost-effectiveness.
1. Prototyping is Easier with CNC Machining
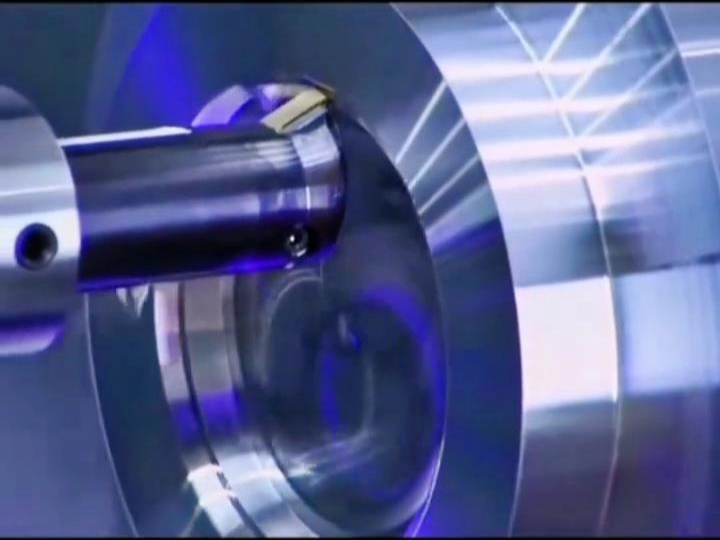
Prototyping is a crucial step in product development, as it allows manufacturers to test designs before committing to full-scale production. CNC machining is often preferred for prototyping because it can produce prototypes from the same materials that will be used in the final product. This gives manufacturers a clear idea of how the final product will perform, especially in terms of strength, durability, and structural integrity.
With CNC machining, accurate testing, and design alterations are possible because the prototypes closely resemble the final product. Since CNC machines work with a variety of materials, manufacturers can easily switch between different materials to test various aspects of the design. 3D printing, in contrast, often uses different materials for prototyping, making it harder to predict how the final product will behave under real-world conditions.
2. Improves Integrity of the Prototype
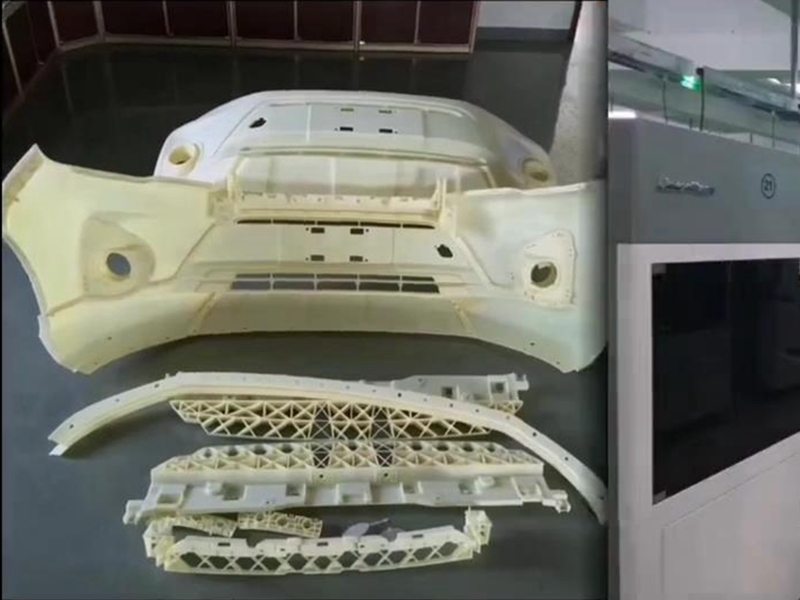

One of the most significant drawbacks of 3D printing is that it applies heat during the manufacturing process, which can weaken the structural integrity of the material. In contrast, CNC machining does not apply heat to the material during production, allowing it to maintain its original strength. This results in parts that are stronger and more durable compared to those produced by 3D printing.
CNC machines can also produce prototypes with greater precision and accuracy, which is essential for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and military, where product integrity is critical.
3. Surface Finish
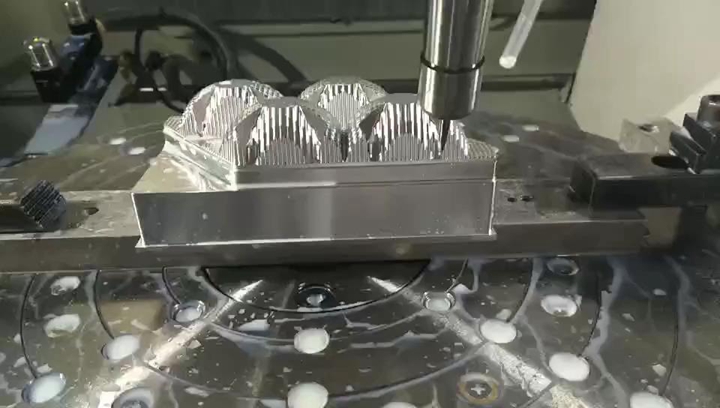

A key advantage of CNC machining is the superior surface finish of the products it creates. Because CNC machines carve parts from solid materials, they produce smooth surfaces with minimal defects. In applications where aesthetics are important—such as consumer products or high-end electronics—CNC machining is the preferred choice.
In contrast, 3D printing often leaves visible layer lines or rough surfaces, which may require additional post-processing to achieve a smooth finish. This extra step adds time and cost to the production process, making 3D printing less efficient for high-quality surface finishes.
4. Higher Tolerance Level
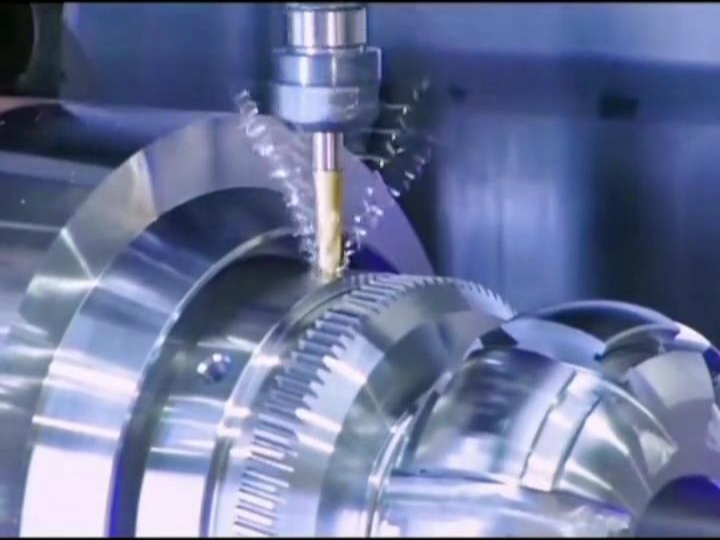

When it comes to precision, CNC machining offers higher tolerances than 3D printing. This means that CNC machines can produce parts with minimal variation from the original design, ensuring a perfect fit in assemblies or components that need to interlock with other parts. In industries where precision is crucial, such as medical devices, aerospace, or robotics, CNC machining’s ability to deliver high-tolerance parts makes it the superior option.
3D printing, on the other hand, is prone to slight dimensional inaccuracies due to its additive process. This can lead to parts that don’t fit together as intended or require additional adjustments after printing.
5. Volume and Price
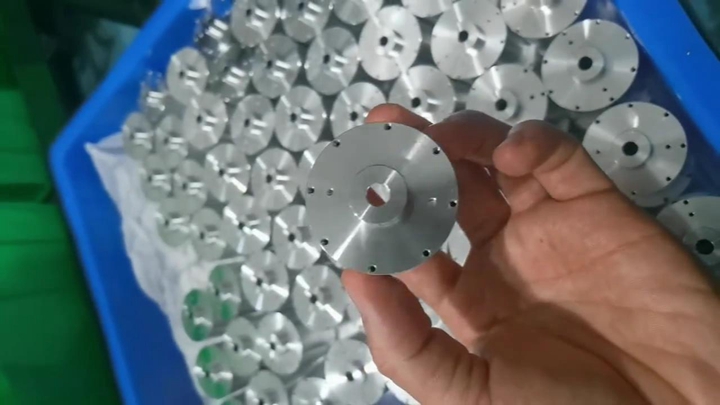

CNC machining is more cost-effective than 3D printing for large-volume production. In CNC machining, the cost per part decreases as production volume increases, making it ideal for mass production. This is particularly important for industries such as automotive or electronics, where large quantities of parts are needed at a low cost.
In contrast, 3D printing is often more expensive for large-scale production because the cost of materials and the time required to produce each part increase with the volume. 3D printing is better suited for small-batch or custom production, where the ability to create unique, one-off designs outweighs the cost.
6. Conclusion
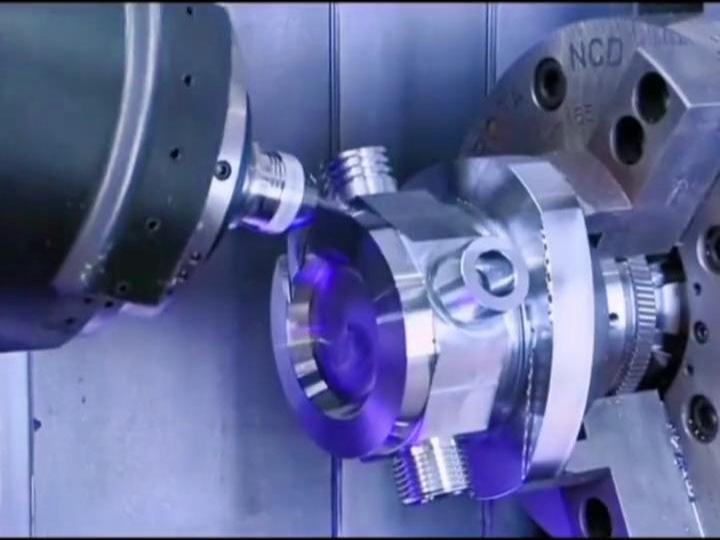
In conclusion, while both CNC machining and 3D printing have revolutionized the manufacturing industry, CNC machining offers several distinct advantages for large-scale production, material strength, precision, and cost-effectiveness. For manufacturers that need to produce high-quality, durable parts with tight tolerances, CNC machining is the superior choice. On the other hand, 3D printing excels in customization, prototyping, and niche applications, but its limitations in material strength and production speed make it less suitable for high-volume manufacturing.
When choosing between CNC machining and 3D printing, it’s essential to consider the specific needs of the project, including material requirements, production volume, and budget. For most large-scale manufacturing applications, CNC machining offers a more efficient, reliable, and cost-effective solution.





